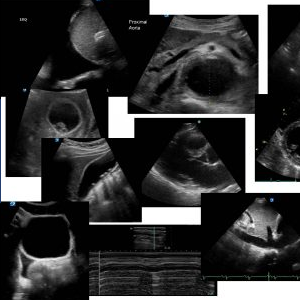
Images by Lee Juan Chiang
A 45 year old diabetic presents with a right hip abscess. This is his ultrasound
With probe compression, pus can be seen moving within the abscess. This is called ‘pus-stalsis” and is diagnostic of an abscess.
Discussion
Skin and soft tissue abscesses account for 2% of ED visits and the incidence is increasing. (1)
For most abscesses, incision and drainage is the definitive treatment, but there is variation between clinicians regarding the optimal treatment strategies for abscess care.
Can clinical examination reliably differentiate between cellulitis underlying abscess?
Not always. It is hard to differentiate between cellulitis and an abscess at times unless there is a clear fluctuant subcutaneous collection. The distinction is important however as the diagnosis will determine management. Antibiotics on the one hand and incision and drainage on the other. Blindly attempting aspiration on a patient who clinically may have an abscess but doesn’t, causes unnecessary pain to the patient and frustration and time-wasting on the part of the doctor.
Where does ultrasound fit in to the management of a suspected abscess?
- Ultrasound can reliably help identify an abscess
- It can distinguish between cellulitis and an abscess
- It can guide aspiration
- It can assess the size and depth of the abcess and therefore guide management (if it is smaller than 1cm, treatment may be to try antibiotics first)
- It has been demonstrated to change management in 14 – 50% of patients with skin and soft tissue infections
- It can be used in serial examinations to evaluate how the pathology, whether cellulitis or an abscess is evolving.
What does an abscess look like on ultrasound?
- It appears as a heterogeneous, anechoic or hypoechoic mass
- If the abscess is hypoechoic, it may be difficut to differentiate from a cyst. A hypoechoic abscess may be associated with posterior enhancement.
- May be compressible and spherical or oval with poorly defined borders
- May have an echogenic capsule
- Fluid movement or “pus -stalsis” on light compression over a suspected cavity is diagnostic.
- Gas collections in an abscess will present as hyperreflective foci which appear in clusters of varying sizes associated with acoustic shadowing and ring-down artifacts
- May have a cobblestone apperance of the surrounding area due to cellulitis
References
- Emergency Medicine Australasia (2015) 27, 460–463 CLINICAL PROCEDURES Emergency department management of skin and soft tissue abscesses Ben BUTSON1,2,3 and Paul KWA1,3