Question 5
Groin lump after angioplasty. Approach and US findings
Approach
The lump should be evaluated clinically for pulsatility and for the presence of bruits or palpable thrill. The differential diagnosis includes
- large haematoma,
- a pseudo aneurysm
- AV fistula• Use a 5 -7.5 MHz linear array probe. May need a 3.5 MHz curvilinear if patient is obese
• Start at the inguinal ligament above the puncture site and then at and below the puncture site.
• Use colour Doppler to evaluate the patency of the femoral artery (FA) and the femoral vein (FV)
• Search the extravascular soft tissues for evidence of large hematomas, pseudo aneurysm or AV fistula
• Adjust colour Doppler gain threshold and flow detection parameters so that colour fills the artery and vein, but does not “bleed over” into the adjacent soft tissues.
• Decrease the gain or increase the pulse repetition frequency (PRF) to visualize the artery and vein if a significant colour Doppler bruit secondary to an AVF is present.
• Adjust gain and threshold to eliminate colour noise artificially written into soft tissues, such as hematomas, which may be confused with PSAs
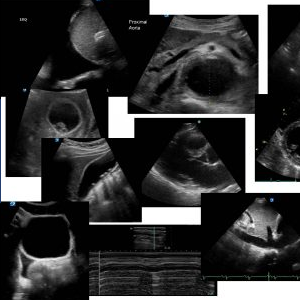
US findings :
Haematoma:
- area of mixed echogenicity, hypo to anechoic
- absence of blood flow with colour Doppler
- may get an inflammatory hypervascularity surrounding the haematoma
- may see an actively bleeding jet
- may be difficult to see the femoral vessels with a linear probe if the haematoma is large because it has displaced them posteriorly.
- may be so extensive that there isn’t a discreet area of haematoma
Visible pseudo aneurysm (PSA) :
- Vascular mass connected to the artery by a neck or tract
- During systole there is antegrade flow into the pseudo aneurysm through the neck
- During diastole, due to the increased pressure in the pseudoaneurysm, there is a retrograde flow out of the pseudoaneurysm through the neck and back into the artery
- This results in a characteristic “to-and-fro” pulsed Doppler waveform in the pseudoaneurysm neck and produces a characteristic “yin-yang” swirling color flow pattern within the body of the PSA
- If the PSA is multilobed you get “a string of pearls’ appearance.
AV fistula:
- Spectral Doppler analysis of the effected artery above the AVF will demonstrate a mono-phasic continuous waveform with elevated systolic and diastolic velocities.
- Flow in the injured artery distal to the AVF will generally have normal pulsatility.
- Spectral Doppler analysis of the affected vein central to the AVF and upstream will demonstrate “arterialized flow” with pulsations during systole and a lack of respiratory phasicity


References:
- Radiology Key : Thoracic key Cardiac catheterisation and intervention
- Radiology Key : Thoracic key Pulsatile Groin Mass in the Postcatheterization Patient