Images by Genevieve Carbonatto
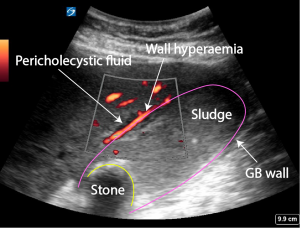
Ultrasound is the best imaging modality to diagnose cholecystitis. Cholecystitis is a frequent presentation to the Emergency department. The hall marks include
- Thickening of the gallbladder wall > 3mm
- Gallstones
- Impacted stones in the cystic duct or gall bladder neck
- Pericholecystic fluid
- +ve Murphy’s sign
- Hyperaemic gallbladder wall on colour or power Doppler.
The following are examples of patients presenting with abdominal pain where a diagnosis of cholecystitis was made:
Case 1.
Ultrasound shows
- Pericholecystic fluid
- thickened GB wall
- Multiple stones
- Sludge


Case 2
Ultrasound shows
- Impacted stone in neck of GB. The stone was only visible when the patient was examined standing
- Thickened GB wall o.45 cm. Stone 2.14 cm


Case 3
Ultrasound shows
- Thickening of gall bladder wall 0.48 cm
- Pericholecystic fluid
- Stone in neck of gall bladder
- Gall bladder perforation (free fluid surrounding GB). Confirmed in theatre. Abdomen full of bile.



Free fluid
Case 4
Ultrasound shows
- GB full of debris
- GB wall thickening
- Pericholecystic fluid
This patient was very ill with fever and abdominal pain. Gallbladders which are full of debris like this may be difficult to identify.

Case 5
Ultrasound shows
- Stone in neck of gallbladder
- Sludge
- Pericholecystic fluid
- GB wall thickening 0.83 cm


Case 6
Ultrasound shows
- Thickened GB wall
- Pericholecystic fluid
- Gall stone in neck of GB ( 2.11 cm)
- Sludge




Case 7
Ultrasound findings
- Thickened gallbladder wall
- Stone in neck of gall bladder
- Pericholecystic fluid
- Sludge fills gall bladder proximal to the impacted stone
- Hyperaemia of wall with power Doppler