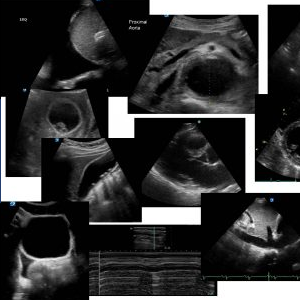
Images by Genevieve Carbonatto
Off axis PLAX left ventricle, (LV) in a “Cavus Excavatum” chest with a prolapse of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve, (MVP).
Off axis PLAX in a “Cavus Excavatum” chest with colour across the mitral valve, (MVP). Note that the colour jet is directed posteriorly with an anterior leaflet MVP.
Apical 4-chamber view. Mitral valve prolapse should not be diagnosed on an Apical 4-chamber only due to the saddle shape of the mitral valve, even a normal valve may appear to be prolapsing.
Apical Long axis ( Apical 3-chamber view) of left ventricle.
Apical 2-chamber view with posterior tilt. Colour across the mitral valve demonstrates two moderate jets of posteriorly directed mitral regurgitation, (MR) consistent with reduced LVOT flow. The descending thoracic aorta can be seen in long axis posterior to the left atrium (LA).